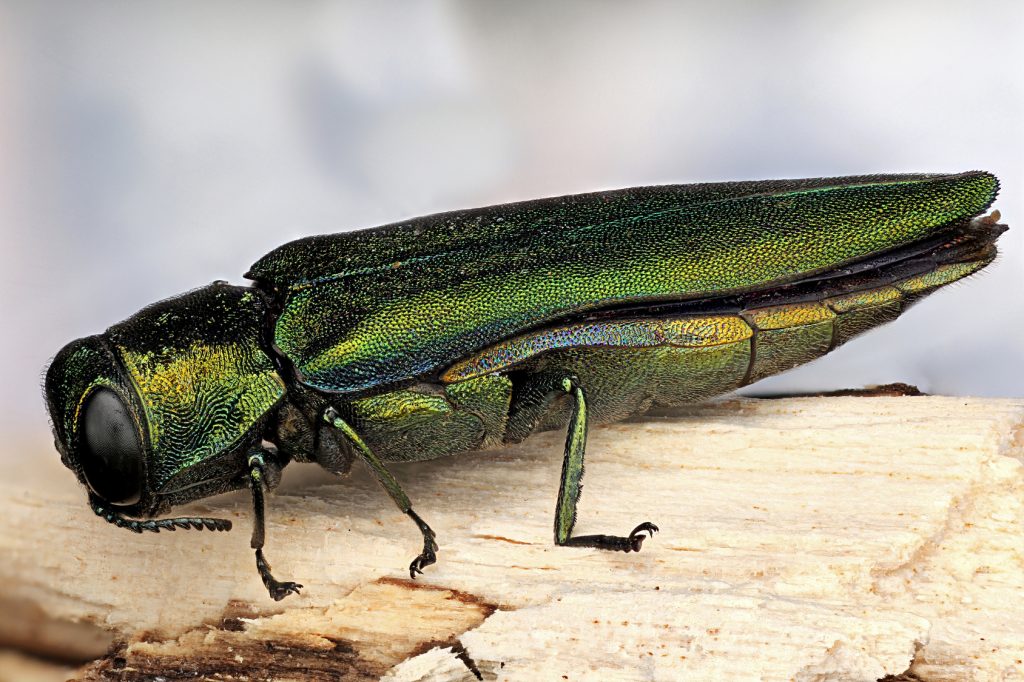
Learn more about the Emerald Ash Borer and what can be done to treat infestations of one of the deadliest tree insects in Illinois
This week, we are returning with our series covering the common tree diseases and insect pests in the Chicago area to take a closer look at an especially destructive pest; the emerald ash borer. The emerald ash borer is one of the most feared tree pests because they can kill formerly healthy trees in just one to two years after infestation. Once an ash tree is infested with the emerald ash borer, there is often little that can be done to save the tree.
The emerald ash borer is an invasive species in North America that is native to regions of northeast Asia. This insect was first seen in North America in the Detroit area in 2002. Scientists believe that they came to North America from China within wooden packaging materials. The emerald ash borer has since spread from Michigan and can be found throughout eastern Canada and the eastern half of the U.S. from Colorado to the east coast and from the northeast and Midwest down to Texas and Louisiana. In the 17 years since the ash borer was discovered in North America, it has killed tens of millions of ash trees which has had a major economic and environmental impact.
The adult emerald ash borer is bright metallic-green in color and is only about half an inch long. Its larvae, which are responsible for most of the damage, are around one inch long when matured and white in color with segmented bodies and flat heads. The larvae damage ash trees by feeding on the wood underneath the bark and boring visible tunnels, known as galleries, that disrupt the flow of water and nutrients within the trees. Infested trees experience dieback of the foliage and branches as well as splitting of the bark.
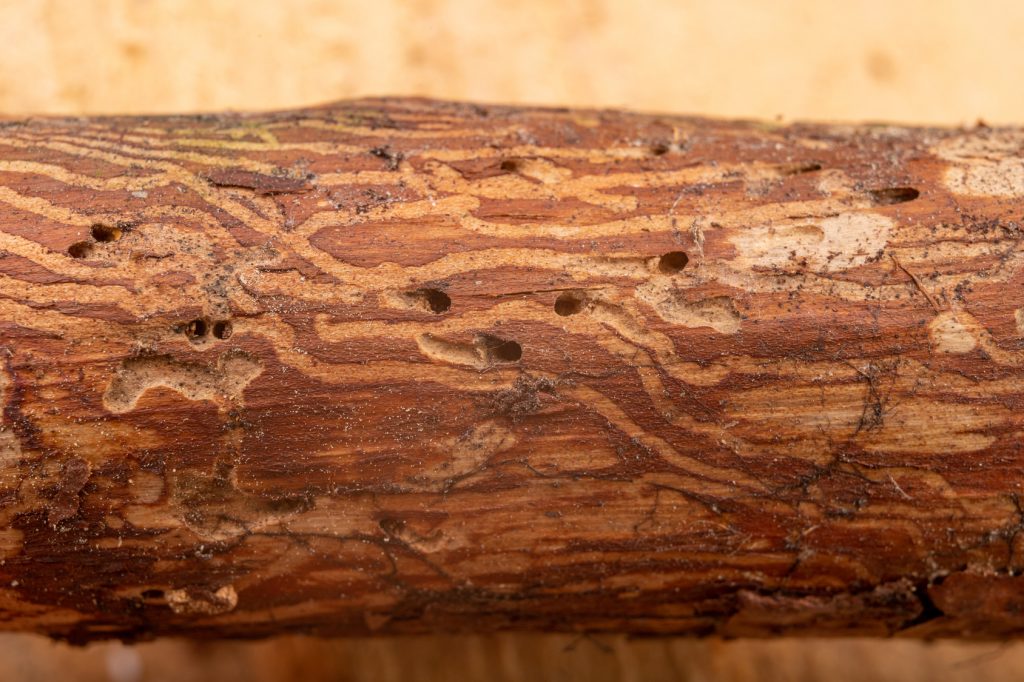

Telltale signs of damage from the Emerald Ash Borer are the “Galleries” that their larvae make beneath the tree bark
While there are treatments available that can help limit the damage of the emerald ash borer to affected ash trees, it is best to prevent your trees from becoming infested. Our arborists at Hendricksen Tree Care provide tree maintenance and preventative treatments to help protect your ash trees from the emerald ash borer and other destructive pests. We will ensure that your trees are properly fertilized to strengthen their natural resistance and we can provide various sprays and injections to treat infected trees. If you do notice any signs of the emerald ash borer on your ash trees, you need to call our tree service professionals immediately to address the infestation.
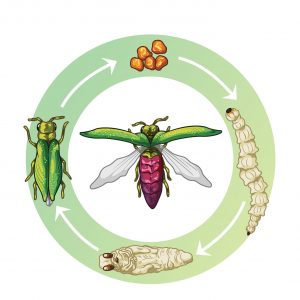
Life Cycle of the Emerald Ash Borer
The average life cycle of the emerald ash borer covers a span of one or two years depending on what time of year the infestation begins. Adult ash borers generally appear in late spring, emerging from infested ash trees after finishing its pupal stage inside the tree. The adults feed on the leaves of the tree for about one week after emerging before mating begins. Trees typically do not suffer much damage from the adults feeding on the canopy.
When it is time to mate, the adult males will fly around the tree looking for females and then drop down to mate. Female emerald ash borers live for about 6 to 8 weeks and mate with multiple males during this time. They can lay between 40 and 200 eggs that are deposited in crevices in the bark. Adult males typically only live for about 4 to 6 weeks after emerging. The eggs are very small in size, one millimeter or less, and they turn a reddish-brown color when fertilized.
Larval Stage
Emerald ash borers cause the most damage in the larval stage. The eggs hatch around two weeks after they are laid, and the larvae immediately start boring through the bark to the inner layers of the tree. They feed in phloem, cambium, and outer xylem, boring tunnels into the wood as they feed. When they are ready to pupate, they will clear a space in the sapwood where they will form into a J-shape. They typically overwinter during this stage and emerge the following spring as adults. In some climates, the larvae might spend an additional year within the tree before emerging the following spring. Mature adults chew D-shaped holes in the outer bark when they are ready to emerge.
Signs of Emerald Ash Borers
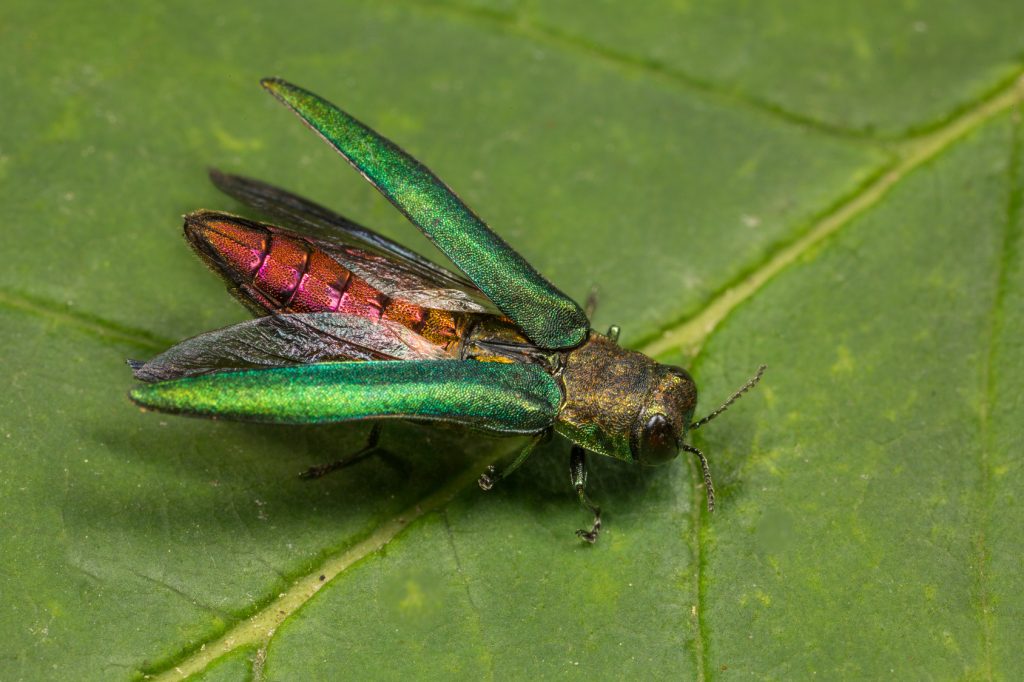

Damage caused by the Emerald Ash Borer is not immediately obvious, and the sign of adult borers does not necessarily mean your tree is already infested, but you should contact an Arborist immediately if you see them
The damage caused by emerald ash borers is not immediately obvious because most of the damage is taking place underneath the bark. As mentioned above, the adults cause little to no damage when feeding on the leaves. Many of the signs of ash borers become more obvious later as the galleries the larvae bore in the sapwood disrupt the flow of water and nutrients.
A tree infested with emerald ash borers may show the following signs of damage:
- D-shaped exit holes on the outer bark where the adults emerged
- Galleries of winding tunnels underneath the bark
- Splitting bark caused by the boring of the larvae
- Dieback of the canopy as the flow of nutrients and water is disrupted
- Suckers may appear towards the base of the tree
When monitoring your ash trees for signs of the borer, look for D-shaped holes and split or loose bark. A surefire sign of an infestation is the presence of the galleries in the sapwood under the bark. An increase in woodpecker activity on your ash trees is also a possible sign as they feed on emerald ash borer larva. You should also look for the bright metallic-green adults feeding on the canopy. Finding adult emerald ash borers does not mean that they have infested the tree yet, but you should call a professional arborist right away.

Once an Ash Tree has signs of the Emerald Ash Borer, it usually means the damage is too severe and the tree will need to be removed
Impact of Emerald Ash Borers
The damage caused by emerald ash borers has environmental and economic effects. Most species of ash trees in North America, including green ash, black ash, and white ash, are vulnerable to damage from the emerald ash borer. The blue ash is the most resistant ash tree species to this insect. The emerald ash borer typically prefers young or stressed ash trees to lay their eggs, but they are also known to infest ash trees that are perfectly healthy. Environmental stressors such as compacted or nutrient deficient soil, urban heat, lack of moisture, and pollution can lower the resistance of ash trees to the emerald ash borer. Ash trees in groups, both naturally occurring and in landscapes, are more vulnerable to infestations than isolated ash trees.
In North America, the emerald ash borer has no natural predators which is why it has been able to spread through most of eastern Canada and the U.S. The elimination of ash trees can disrupt the natural ecosystem by affecting other species that rely on the ash tree for food and shelter. The loss of ash trees can also change the composition of the soil and allow invasive plants to thrive.
The economic impact of the loss of ash trees can be felt by local governments, businesses, and homeowners. Businesses that sell products made from ash wood are affected by quarantines that can limit the production and transport of ash products. Local and state governments must spend billions in some areas to remove infested ash trees. If an ash tree is infested on private property, this cost falls on homeowners.
Emerald Ash Borer Control
As mentioned above, there is often little that can be done to save a tree infested with the emerald ash borer. However, control measures can be taken to reduce the damage to infested trees and prevent the infestations from spreading.
The following are the most effective emerald ash borer treatment and control methods:
- Quarantine and removal: When an emerald ash borer infestation occurs, local and state governments will likely impose a quarantine to help prevent the spread of such infestations. Transport of ash wood outside of the quarantined areas is prohibited in case the wood has live emerald ash borer larvae. Infested trees are often removed in urban areas and replaced with a different tree species while infested trees in rural areas are harvested for lumber or firewood. If an infested tree on private property needs to be removed, it is best to have a professional provide tree removal.
- Insecticides: Insecticides can be used to treat and prevent emerald ash borer infestations, but they are only used for infested trees in urban areas. Insecticides are typically injected directly into the tree or soil drench and they are effective for 1 to 3 years. If a tree is infected with insecticides after an infestation has begun, they may experience further damage. It is best for a professional arborist to apply these insecticides.
- Biological control: As we have already stated, the emerald ash borer has no natural predators in North America. In 2007, the USDA approved the import and release of four different species of non-stinging wasps that are natural predators of the emerald ash borer. A couple of these species have been able to increase their populations in the U.S. and have had some success controlling emerald ash borer populations.
Emerald Ash Borer Prevention, Treatment Options and Control from Hendricksen Tree Care

Don’t let the Emerald Ash Borer be the end of your Ash Trees. Contact a professional arborist such as Hendricksen Tree Care today to learn about your Emerald Ash Borer treatment options today
Since its appearance in North America, the emerald ash borer has caused significant damage that has led to the removal of millions of ash trees. The tree removal has cost homeowners and governments billions of dollars and negatively impacted local ecosystems. If you have ash trees on your property, it is very important that you have your trees treated to prevent infestations and look for signs of the emerald ash borer so you can take action right away.
At Hendricksen Tree Care, we take emerald ash borer infestations very seriously. Our arborists will provide your ash trees with preventative insecticide treatments and check your trees regularly for signs of an infestation so we can act quickly. We can help treat Chicagoland ash trees in Arlington Heights, Northbrook, Lake Zurich, Park Ridge, Mount Prospect, Barrington, and the surrounding north and northwest Chicago suburbs.
Look for our next installment of our series on the common tree diseases and insect pests in the Chicago area.